Aerobic conditioning is a crucial component of overall physical fitness, offering numerous health benefits to both new and average runners. By engaging in regular aerobic exercise, individuals can improve their cardiorespiratory fitness, cognitive function and weight management – all key elements of physical health. In this blog post, we will delve into the numerous advantages of aerobic training and provide a comprehensive guide to different types of exercises for various fitness levels, goal-setting tips, and nutrition advice tailored for cardiovascular fitness.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover different types of aerobic exercises that cater to various fitness levels and preferences. We will also discuss how to set achievable goals for enhancing your aerobic capacity and provide valuable insights on nutrition specifically tailored for cardiovascular fitness. Finally, we will delve into recovery strategies that ensure optimal progress in your aerobic conditioning journey while minimizing the risk of injury or burnout.
Quick Navigation
1. Benefits of Aerobic Conditioning
It refers to exercises that increase your heart rate and improve your body’s ability to use oxygen efficiently. By engaging in aerobic conditioning, runners can experience numerous benefits to their running performance, including improved cardiovascular health.
Improved Cardiovascular Health
One of the primary advantages of aerobic exercise is its positive impact on cardiovascular health. Regular aerobic workouts strengthen your heart muscles, allowing it to pump blood more effectively throughout your body. This leads to better circulation and improved endurance during runs.
Increase in Lung Capacity
Aerobic activities also help boost lung capacity by enhancing respiratory efficiency. As you engage in consistent aerobic training, your lungs become stronger and capable of taking in more oxygen with each breath. This increased oxygen intake translates into greater stamina when running long distances.
Fat Burning and Weight Management
- Fat burning: Aerobic exercise has been proven effective at burning fat stores for energy during prolonged periods of activity – making it essential for runners looking to shed excess weight or maintain their current physique.
- Weight management: Incorporating regular cardio sessions into your routine can help keep unwanted pounds at bay while building lean muscle mass necessary for optimal running performance.
Mental Health Benefits

Beyond physical improvements, engaging in regular aerobic conditioning offers several mental health perks as well. Studies have shown that consistent cardiovascular exercise helps reduce stress levels, alleviate symptoms associated with anxiety and depression, and even boost cognitive function.
Reduced Risk of Injury
Last but not least, a well-rounded aerobic conditioning program can help decrease the likelihood of running-related injuries. By strengthening your cardiovascular system and improving overall fitness levels, you’ll be better equipped to handle the demands placed on your body during runs – reducing strain on muscles, joints, and ligaments.
Incorporating aerobic conditioning into your training regimen is essential for reaping these numerous benefits. As you progress in your running journey, make sure to prioritize this crucial aspect of fitness.
Aerobic conditioning provides numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular and respiratory function. Moving on to the next heading, let’s explore the different types of aerobic exercise available.
Key Takeaway:
Aerobic conditioning is vital for runners as it improves cardiovascular health, increases lung capacity, aids in fat burning and weight management, offers mental health benefits, and reduces the risk of injury. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart muscles allowing better circulation leading to improved endurance during runs. Incorporating regular cardio sessions into your routine can help keep unwanted pounds at bay while building lean muscle mass necessary for optimal running performance.
2. Types of Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic conditioning is essential for runners as it helps improve endurance and overall performance. There are various types of aerobic exercises that can benefit your running routine. In this part, we will examine various aerobic exercises and their potential to improve your running.
Steady-State Running
Steady-state running involves maintaining a consistent pace throughout the entire workout session. Performing steady-state running can enable your body to better use oxygen during exercise, thus enhancing cardiovascular fitness and endurance. Incorporating steady-state runs into your training plan will help increase your stamina and make longer distances more manageable.
Interval Training
Interval training consists of alternating between periods of high-intensity effort followed by recovery intervals at a lower intensity or complete rest. Interval training has been demonstrated to enhance cardiovascular fitness, augment speediness, and incinerate more calories than usual steady-state workouts. Including interval sessions in your weekly schedule can help you break through plateaus and reach new personal bests in races.
Fartlek Workouts
The term fartlek, which means “speed play” in Swedish, refers to an unstructured form of interval training where you vary the intensity based on how you feel during the run rather than following a set pattern or time frame (source). Fartlek workouts can be an enjoyable way to add variety and spontaneity to your aerobic conditioning routine, as they allow you to experiment with different paces and distances.
Tempo Runs
Tempo runs are designed to help improve your lactate threshold, which is the point at which lactic acid begins accumulating in the bloodstream faster than it can be removed. By running at a pace slightly below this threshold for extended periods, you train your body to become more efficient at processing lactic acid. This results in reduced fatigue during longer races and improved overall performance.
Incorporating these various types of aerobic exercises into your training plan will not only enhance your running abilities but also keep things fresh and engaging. Experiment with each form of exercise and find what works best for you on your journey towards becoming a stronger runner. Regular aerobic exercise can help improve your aerobic capacity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and cardiovascular fitness. It is an essential part of maintaining physical fitness and overall health. Exercise habits that include moderate-intensity aerobic training can help you lose weight and improve your perceived exertion during training sessions. Additionally, aerobic exercise has been shown to improve cognition and blood flow in healthy adults, providing numerous health benefits.
Realizing the various sorts of aerobic exercise is pivotal to exploiting its advantages as a fundamental piece of any sprinter’s preparation routine. Setting goals for aerobic conditioning will help you make sure that your workouts are effective in helping you reach your running objectives.
Key Takeaway:
Aerobic conditioning is crucial for runners to improve endurance and performance. Steady-state running, interval training, fartlek workouts, and tempo runs are some popular forms of aerobic exercise that can benefit a runner’s routine by increasing stamina, boosting cardiovascular fitness, improving lactate threshold, and adding variety to the workout. Regular aerobic exercise not only enhances running abilities but also provides numerous health benefits such as weight loss and improved cognition.
3. Setting Goals for Aerobic Conditioning
Understanding how to set realistic goals for aerobic conditioning and track your progress is crucial in improving your running performance. By setting achievable targets, you’ll stay motivated and enjoy the process of building a strong aerobic base.
A. Determine Your Baseline Fitness Level
To begin with, assess your current fitness level by performing an aerobic fitness test. This will give you a baseline to measure future improvements against. You can choose from various tests such as timed runs or heart rate-based assessments.
B. Set SMART Goals
When setting goals for aerobic conditioning, use the SMART criteria: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound: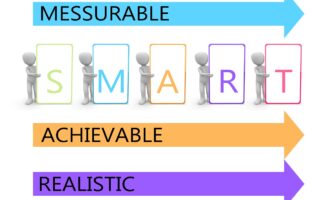
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., increase weekly mileage).
- Measurable: Make sure your goal can be quantified (e.g., run 20 miles per week).
- Achievable: Ensure that the goal is challenging but attainable based on your current fitness level.
- Relevant: Your goal should align with your overall running objectives (e.g., preparing for a half marathon).
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goal (e.g., increase weekly mileage by 10% within the next 4 weeks).
C. Monitor Progress Regularly
Keep track of your aerobic conditioning progress by logging your workouts and periodically reassessing your fitness level. You can use a running app or a simple spreadsheet to record details such as distance, time, and heart rate.
D. Adjust Goals As Needed
As you make progress in your aerobic conditioning journey, don’t be afraid to adjust your goals accordingly. If you find that you’re progressing faster than anticipated, consider setting more challenging targets. Conversely, if you’re struggling to meet the initial objectives, reevaluate them and set more realistic expectations.
Incorporating these goal-setting strategies into your aerobic conditioning plan will help ensure consistent improvement in both endurance and overall running performance.
Setting goals for aerobic conditioning is an important step in any runner’s journey, as it provides motivation and direction to help you reach your desired fitness level. Having a suitable dietary regimen can help you progress towards attaining your target of augmented aerobic capability.
Key Takeaway:
To improve running performance, it’s important to set achievable goals for aerobic conditioning using the SMART criteria and regularly monitor progress through logging workouts. Adjusting goals as needed will ensure consistent improvement in endurance and overall performance.
4. Nutrition for Aerobic Conditioning
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in fueling your aerobic conditioning workouts and helping you achieve optimal results.  Consuming the correct sustenances can improve your vitality levels, advance more noteworthy perseverance and help in quicker recuperation. To maximize your aerobic training results, here we will explore the most beneficial food choices.
Consuming the correct sustenances can improve your vitality levels, advance more noteworthy perseverance and help in quicker recuperation. To maximize your aerobic training results, here we will explore the most beneficial food choices.
A. Carbohydrates: The Main Energy Source
Carbohydrates are essential for runners, as they provide the primary source of energy during aerobic exercise. Consuming an adequate amount of carbs helps maintain glycogen stores in muscles and prevents early fatigue. Some excellent sources of carbohydrates include:
- Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa)
- Fruits (e.g., bananas, apples)
- Vegetables (e.g., sweet potatoes, peas)
- Dairy products (e.g., yogurt, milk)
B. Protein: Essential for Muscle Repair and Growth
Protein is vital for runners, as it aids in muscle repair and growth after intense workouts or long runs. Consuming enough protein ensures that your body has the necessary building blocks to rebuild damaged tissues efficiently. Good sources of protein include:
- Poultry (e.g., chicken breast or turkey slices)
- Fish (e.g., salmon, tuna)
- Lean meats (e.g., lean beef or pork tenderloin)
- Plant-based proteins (e.g., beans, lentils, tofu)
C. Healthy Fats: For Long-lasting Energy and Overall Health
Healthy fats are important for runners, as they provide long-lasting energy and support overall health. Including healthy fats in your diet can help improve endurance during longer runs by providing a slow-burning fuel source. Some great options for healthy fats include:
- Avocadoes
- Nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts)
- Seeds (e.g., chia seeds, flaxseeds)
- Olive oil or coconut oil
In addition to these macronutrients, don’t forget to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day and consuming electrolytes during extended workouts.
To maximize aerobic conditioning, it is essential to ensure adequate nutrition in order to provide energy for exercise. Moving on from this topic, recovery strategies are also necessary in order to maximize the benefits of aerobic conditioning.
Key Takeaway:
Proper nutrition is crucial for aerobic conditioning workouts. Carbohydrates provide the primary source of energy, protein aids in muscle repair and growth, and healthy fats provide long-lasting energy. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day and consuming electrolytes during extended workouts is important.
5. Recovery Strategies for Aerobic Conditioning
Recovery is an indispensable element of aerobic conditioning, enabling the body to adjust and become more powerful after each exercise session. In this section, we will explore various recovery strategies that can help you get the most out of your aerobic training sessions.
Active Recovery
Active recovery involves performing low-intensity exercises on rest days or immediately following a workout. This helps increase blood flow to the muscles, promoting faster healing and reducing soreness. Examples include walking, cycling, swimming or practicing yoga.
Sleep Quality
 Adequate sleep is crucial for proper muscle repair and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support optimal recovery from aerobic workouts. Consider creating a consistent bedtime routine and maintaining a comfortable sleeping environment to improve your sleep hygiene.
Adequate sleep is crucial for proper muscle repair and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support optimal recovery from aerobic workouts. Consider creating a consistent bedtime routine and maintaining a comfortable sleeping environment to improve your sleep hygiene.
Nutrition & Hydration
- Protein: Consuming protein within 30 minutes post-workout supports muscle repair and growth. Opt for high-quality sources of protein such as lean meats, fish, dairy products or plant-based alternatives like tofu or tempeh to support muscle repair and growth within 30 minutes post-workout.
- Carbohydrates: Replenish glycogen stores by consuming carbohydrates shortly after exercise – whole grains, fruits and starchy vegetables are excellent choices.
- Fats:Incorporate healthy fats into your diet (e.g., avocados, nuts) which provide long-lasting energy while also supporting hormone production and reducing inflammation.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated throughout the day by drinking water or electrolyte-rich beverages, especially after intense aerobic workouts to replace lost fluids and minerals.
Foam Rolling & Stretching
Regularly using a foam roller can help release muscle tension and improve flexibility. Additionally, incorporating static stretching post-workout or dynamic stretching before your runs may reduce the risk of injury while promoting better range of motion.
Scheduling Rest Days & Listening to Your Body
Avoid overtraining by scheduling rest days into your training plan – these allow for proper recovery and adaptation. Pay attention to signs of fatigue or pain, adjusting your workout intensity accordingly. Remember that consistency is key in aerobic conditioning; it’s better to take an extra rest day than push through discomfort and risk injury.
Key Takeaway:
To get the most out of your aerobic training sessions, it’s important to incorporate recovery strategies. These include active recovery exercises like walking or yoga, getting adequate sleep and proper nutrition, foam rolling and stretching regularly, scheduling rest days into your training plan, and listening to your body by adjusting workout intensity when necessary. Remember that consistency is key in achieving optimal results while avoiding injury.
FAQs in Relation to Aerobic Conditioning
What is Aerobic Conditioning?
Aerobic conditioning refers to the process of improving your cardiovascular system’s efficiency and endurance through various forms of aerobic exercises. This type of training increases your heart rate, strengthens your heart muscles, and enhances oxygen delivery to working muscles.
Why is Aerobic Conditioning Important?
Aerobic conditioning is essential for overall health and fitness as it improves cardiovascular endurance, reduces risk factors for chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes, aids in weight management, boosts mood and mental well-being, increases energy levels, and promotes better sleep quality.
Where Can I Find Scholarly Articles on Aerobic Exercise?
You can find scholarly articles on aerobic exercise from reputable sources such as PubMed, ScienceDirect, or Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise Journal. These resources provide research-based information on various aspects of aerobic training including its benefits and mechanisms behind improvements in performance or health outcomes.
What is Aerobic Conditioning Primarily Designed to Improve?
Aerobic conditioning is primarily designed to improve cardiovascular endurance by enhancing the efficiency with which your body delivers oxygen-rich blood to working muscles. This results in increased stamina during prolonged physical activities while reducing fatigue rates over time.
Conclusion
To reach optimal performance, a comprehensive aerobic conditioning regimen should be included in any runner’s training program. It improves cardiovascular health, endurance, and overall fitness levels. By incorporating different types of aerobic exercises such as running, cycling, or swimming and setting achievable goals for yourself while fueling your body with proper nutrition and allowing time for recovery strategies, you can optimize the benefits of aerobic conditioning.
At The Runner’s Base, we are dedicated to helping runners achieve their fitness goals through our expert advice on training programs, injury prevention techniques, and nutrition plans tailored to each individual. Join us today in taking your running performance to the next level with Aerobic Conditioning!
Ready to start improving your aerobic capacity? Check out The Runner’s Base for personalized training plans that will help you reach new heights in your running journey.

